Understanding cobby's Change Notification System
This article explains the architecture behind cobby's change notification system and how data synchronization works between Magento and cobby.
How Change Notification Works
The change notification system in cobby is built on Magento's event-driven architecture. Understanding this flow helps you troubleshoot synchronization issues and understand why changes appear in the system.
The Notification Flow
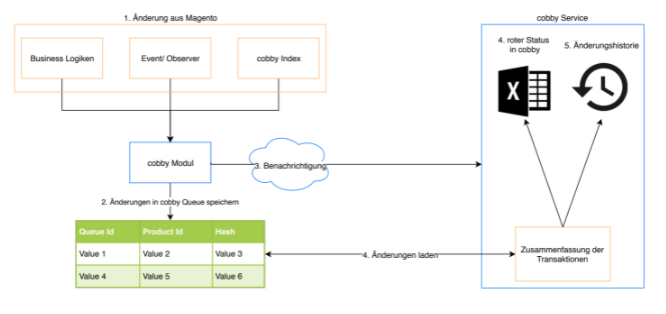
When a change occurs in Magento, the system follows this sequence:
- Change Detection: Magento's model layer detects the modification (product, category, or attribute change)
- Event Broadcasting: The model informs all dependent business logic through either:
- The cobby Indexer
- Magento's native Event/Observer system
- Queue Entry: The changed elements are added to the cobby queue within Magento, each receiving a unique queue ID
- Service Notification: The cobby service is notified of pending changes
- Transaction Processing: cobby loads all queue entries and processes them together in a single transaction (transaction ID)
- Status Update: Affected products receive a red status in Excel if the application is open
- History Recording: The change appears in the cobby customer center's change history with the queue ID as the transaction ID
Why This Architecture Matters
This event-driven architecture ensures:
- Consistency: All business logic is properly informed of changes
- Traceability: Every change gets a unique identifier for tracking
- Real-time Updates: Changes are communicated immediately to cobby
- Transaction Integrity: Multiple changes are processed together atomically
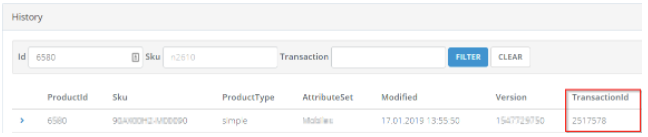
Understanding Transaction IDs
The transaction ID reveals the origin of a change:
- Magento-originated changes: Consecutive numbered IDs (e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4...)
- cobby-originated changes: Unique, non-sequential IDs
This distinction helps you identify whether a change came from direct Magento editing or through cobby.
When the System Can Fail
The notification system relies on Magento's model layer being properly used. In rare cases, problems can occur when:
Bypassing the Model Layer
Some extensions or direct database modifications can bypass Magento's model layer entirely. When this happens:
- The cobby indexer and event observers are not triggered
- Changes don't appear in cobby
- The Magento backend and cobby show different values
- Other Magento functions may also malfunction
Important: While this issue is often first noticed in cobby, it typically affects all Magento functionality because the business logic layer is unaware of the changes.
Troubleshooting Discrepancies
When you notice different values between Magento and cobby:
- Check the change history to identify when the discrepancy occurred
- Look for manual database entries or problematic extensions
- Verify that the extension properly uses Magento's model layer
The change history is your primary diagnostic tool for understanding when and how synchronization issues occurred.
Why Understanding This Matters
Understanding the change notification architecture helps you:
- Diagnose synchronization problems quickly
- Identify problematic extensions or customizations
- Understand the root cause of data discrepancies
- Communicate effectively with developers about issues
The system is designed to be reliable, but understanding its architecture helps you recognize when something is working outside normal patterns.
Related Topics
For practical guidance on working with the change history, see the How-To guides for:
- Using the product history feature
- Troubleshooting synchronization issues
- Working with the job history
For technical specifications on the queue system, see the Reference documentation.